Difference Between A Vector And Raster In Gis Denisengineer

Vector Vs Raster By Suhasni Pdf Graphics Image Processing The two primary types of spatial data are vector and raster data in a gis. but what is the difference between raster and vector data? when should we use raster and when should we use vector features? find out more about the spatial data models commonly used. The core distinction lies in how they represent geographical features: raster data uses a grid of cells, while vector data uses points, lines, and polygons. this simple difference leads to a wide range of implications in how each is best used.

Difference Between Vector And Raster Gis Sakibc The fundamental difference between raster and vector data models in geographic information systems (gis) lies in how they represent spatial data. the vector model uses points, lines, and polygons to define locations and shapes on the earth, while the raster model employs a grid of cells or pixels to represent geographic space. In essence, vector data uses points, lines, and polygons to define the locations and shapes of geographic features, while raster data employs a grid of cells or pixels to represent geographic variation across a continuous surface. The difference between vector and raster data in gis. in this article, we will cover the fundamental differences between raster and vector data. geospatial data can be represented using either vector data type or raster. The main difference between raster and vector data in gis is how they store spatial information. raster data uses pixels to represent continuous features, while vector data uses geometric shapes to represent specific locations and boundaries.
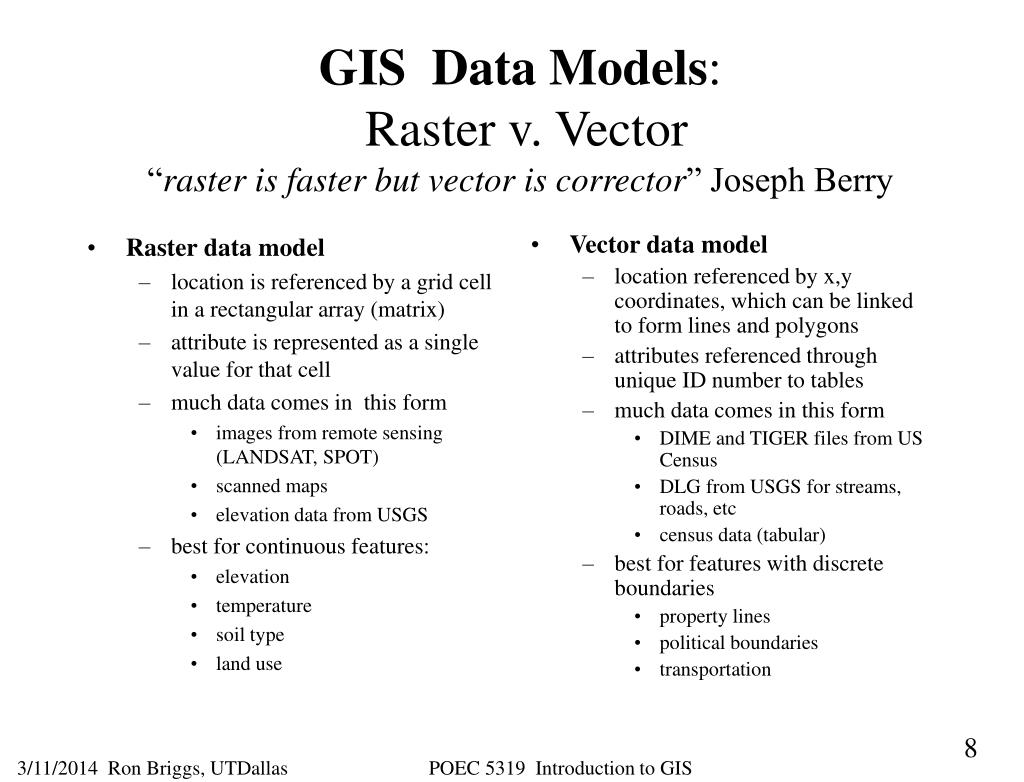
Difference Between Vector And Raster Gis Hetyall The difference between vector and raster data in gis. in this article, we will cover the fundamental differences between raster and vector data. geospatial data can be represented using either vector data type or raster. The main difference between raster and vector data in gis is how they store spatial information. raster data uses pixels to represent continuous features, while vector data uses geometric shapes to represent specific locations and boundaries. Vector data represent geographic features using precise mathematical coordinates, defining spatial objects through fundamental geometric primitives: points, lines, and polygons. each vector element contains exact location information and can include rich attribute data. Raster giss (grid cell) work by storing attribute data as grid cell values. raster giss have superior analytical power to vector giss, but grid cell map presentation tends to be less attractive than vector map presentation. choosing an appropriate cell resolution can be tricky. Raster data and vector data are two common types of spatial data used in geographic information systems (gis). raster data is made up of a grid of cells, where each cell represents a specific value or attribute. this type of data is best suited for continuous data such as elevation or temperature. Vector data, raster data, images, triangular irregular networks (tins), and terrain datasets are all apart of spatial data. attribute data is made up of details such as the information that explains “where”, “what”, and “why”. it provides characteristics about the spatial data.

Difference Between Vector And Raster Gis Eastolfe Vector data represent geographic features using precise mathematical coordinates, defining spatial objects through fundamental geometric primitives: points, lines, and polygons. each vector element contains exact location information and can include rich attribute data. Raster giss (grid cell) work by storing attribute data as grid cell values. raster giss have superior analytical power to vector giss, but grid cell map presentation tends to be less attractive than vector map presentation. choosing an appropriate cell resolution can be tricky. Raster data and vector data are two common types of spatial data used in geographic information systems (gis). raster data is made up of a grid of cells, where each cell represents a specific value or attribute. this type of data is best suited for continuous data such as elevation or temperature. Vector data, raster data, images, triangular irregular networks (tins), and terrain datasets are all apart of spatial data. attribute data is made up of details such as the information that explains “where”, “what”, and “why”. it provides characteristics about the spatial data.
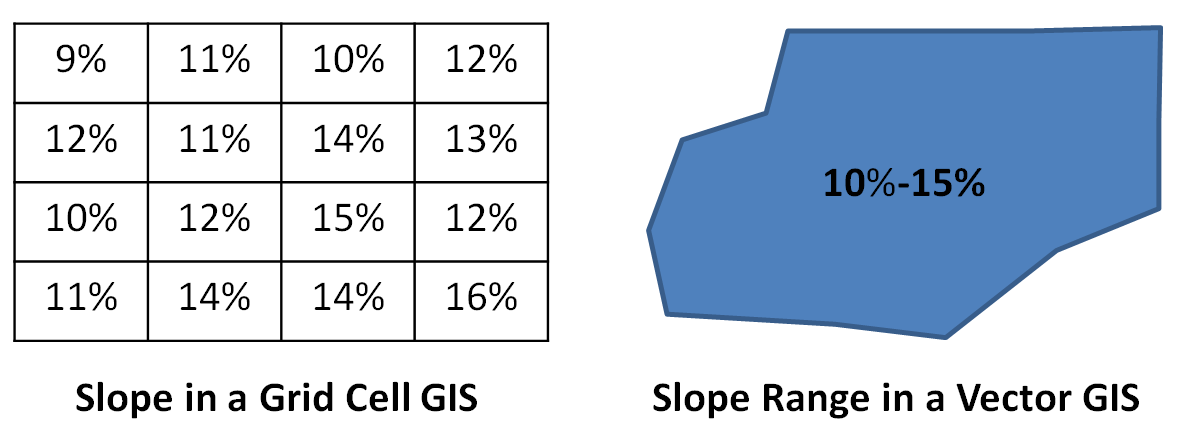
Raster Vs Vector Gis Gis University Raster Vs Vector Gis Raster data and vector data are two common types of spatial data used in geographic information systems (gis). raster data is made up of a grid of cells, where each cell represents a specific value or attribute. this type of data is best suited for continuous data such as elevation or temperature. Vector data, raster data, images, triangular irregular networks (tins), and terrain datasets are all apart of spatial data. attribute data is made up of details such as the information that explains “where”, “what”, and “why”. it provides characteristics about the spatial data.

Comments are closed.