Viral Vector Models
Vector Viral In this review, we will describe three viral vector platforms that have gained wide use for efficacious gene therapy and regulatory approval. these three strategies are based on ads, aavs,. Viral vectors can express foreign proteins at high levels in host cells, resulting in strong, long lasting immune responses against the target proteins. this chapter describes the use of virus vectors in the context of vaccination against human pathogens. various vector platforms are discussed, compared, and contrasted. introduction.

Viral Vector Models To date, 5 main classes of viral vectors have been tested for clinical applications. 25, 27 these include retroviruses (rv), adenoviruses (av), adeno associated viruses (aav), lentiviruses (lv), and herpes simplex viruses (hsv). 8, 28 although many viral vectors are safe and effective delivery vehicles for clinical gene therapy, some viral vecto. We present a variational autoencoder (proteinvae) that can generate synthetic viral vector serotypes without epitopes for pre existing neutralizing antibodies. Further, we describe the different viral vector based pd models currently available based on overexpression strategies for autosomal dominant genes such as α synuclein and lrrk2, and knockout or knockdown strategies for autosomal recessive genes, such as parkin, dj 1, and pink1. Further, we describe the different viral vector based pd models currently available based on overexpression strategies for autosomal dominant genes such as α synuclein and lrrk2, and knockout or knockdown strategies for autosomal recessive genes, such as parkin, dj 1, and pink1.

Viral Vector At Vectorified Collection Of Viral Vector Free For Further, we describe the different viral vector based pd models currently available based on overexpression strategies for autosomal dominant genes such as α synuclein and lrrk2, and knockout or knockdown strategies for autosomal recessive genes, such as parkin, dj 1, and pink1. Further, we describe the different viral vector based pd models currently available based on overexpression strategies for autosomal dominant genes such as α synuclein and lrrk2, and knockout or knockdown strategies for autosomal recessive genes, such as parkin, dj 1, and pink1. Here we review the recent developments in viral vector technologies, focusing on novel vectors based on primate derived adenoviruses and poxviruses, rhabdoviruses, paramixoviruses, arenaviruses and herpesviruses. Viral vectors (in most cases lentiviral or aav vectors) are unilaterally injected in the sn to overexpress pathogenic proteins in neurons. after virus injection, an 8 to 16 week period is usually needed for the lesion to fully develop. Af viral sequence classification is considerably faster than alignment based techniques. moreover, the ability to train models and classify viral sequences using only modest computational resources, without reliance on cloud infrastructure, underscores the accessibility and scalability of these methods for researchers worldwide. The genslms model proposes adapting language models for genomic sequences, demonstrating the ability to rapidly identify emerging variants by learning evolutionary patterns from millions of viral.
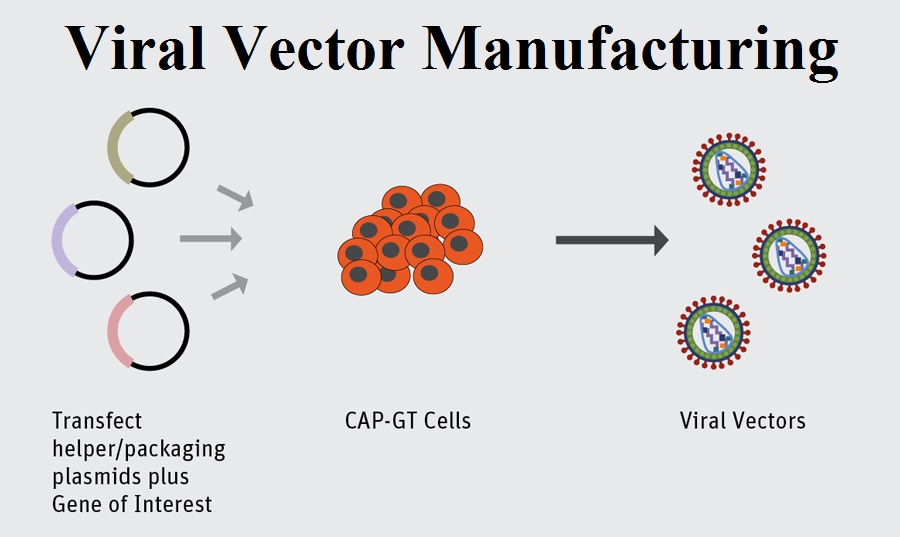
Viral Vector At Vectorified Collection Of Viral Vector Free For Here we review the recent developments in viral vector technologies, focusing on novel vectors based on primate derived adenoviruses and poxviruses, rhabdoviruses, paramixoviruses, arenaviruses and herpesviruses. Viral vectors (in most cases lentiviral or aav vectors) are unilaterally injected in the sn to overexpress pathogenic proteins in neurons. after virus injection, an 8 to 16 week period is usually needed for the lesion to fully develop. Af viral sequence classification is considerably faster than alignment based techniques. moreover, the ability to train models and classify viral sequences using only modest computational resources, without reliance on cloud infrastructure, underscores the accessibility and scalability of these methods for researchers worldwide. The genslms model proposes adapting language models for genomic sequences, demonstrating the ability to rapidly identify emerging variants by learning evolutionary patterns from millions of viral.

Comments are closed.