Visualizing Vectors In 2 Dimensions Two Dimensional Motion Physics Khan Academy

Two Dimensional Motion And Vectors Pdf Euclidean Vector Velocity Visualizing, adding and breaking down vectors in 2 dimensions. created by sal khan. watch the next lesson: khanacademy.org science p missed the previous lesson?. Khan academy khan academy.

Week003 Vectors And Two Dimensional Motion Download Free Pdf About khan academy: khan academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that empower learners to study at their own pace in and outside of the. This video describes how to convert vectors from magnitude direction form into component form, and vice versa. Review the skills for analyzing vectors, including how to find horizontal and vertical components of vectors. to simplify calculations for two dimensional motion, we analyze the movement in the vertical direction separately from the horizontal direction. Resources videos visualizing vectors in 2 dimensions | two dimensional motion | physics | khan academy remote video url.
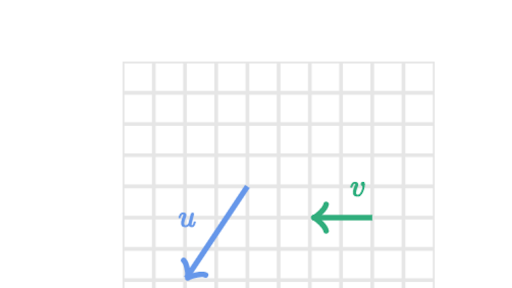
Describing Two Dimensional Motion With Vectors Practice Khan Academy Review the skills for analyzing vectors, including how to find horizontal and vertical components of vectors. to simplify calculations for two dimensional motion, we analyze the movement in the vertical direction separately from the horizontal direction. Resources videos visualizing vectors in 2 dimensions | two dimensional motion | physics | khan academy remote video url. The key to analyzing two dimensional projectile motion is to break it into two motions, one along the horizontal axis and the other along the vertical. to describe motion we must deal with velocity and acceleration, as well as with displacement. Key insights 🦾 one dimensional problems can be extended to two dimensions, but most classical mechanics problems can be solved using up to three dimensions. 🤕 vector addition in two dimensions involves visually shifting vectors and connecting their tails and heads. Two dimensional motion looks at how an object moves in two directions at once. we analyze this motion by separating it into horizontal and vertical components. kinematic equations describe the motion of objects. in two dimensional motion, these are used separately for each component. For two dimensional motion, the path of an object can be represented with three vectors: one vector shows the straight line path between the initial and final points of the motion, one vector shows the horizontal component of the motion, and one vector shows the vertical component of the motion.
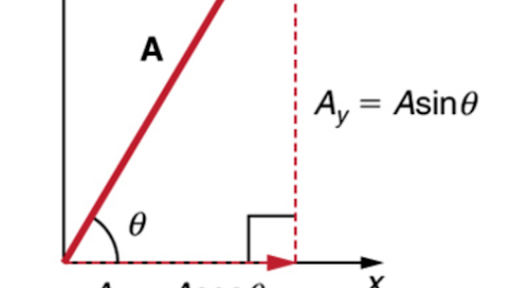
Analyzing Vectors Using Trigonometry Review Article Khan Academy The key to analyzing two dimensional projectile motion is to break it into two motions, one along the horizontal axis and the other along the vertical. to describe motion we must deal with velocity and acceleration, as well as with displacement. Key insights 🦾 one dimensional problems can be extended to two dimensions, but most classical mechanics problems can be solved using up to three dimensions. 🤕 vector addition in two dimensions involves visually shifting vectors and connecting their tails and heads. Two dimensional motion looks at how an object moves in two directions at once. we analyze this motion by separating it into horizontal and vertical components. kinematic equations describe the motion of objects. in two dimensional motion, these are used separately for each component. For two dimensional motion, the path of an object can be represented with three vectors: one vector shows the straight line path between the initial and final points of the motion, one vector shows the horizontal component of the motion, and one vector shows the vertical component of the motion.
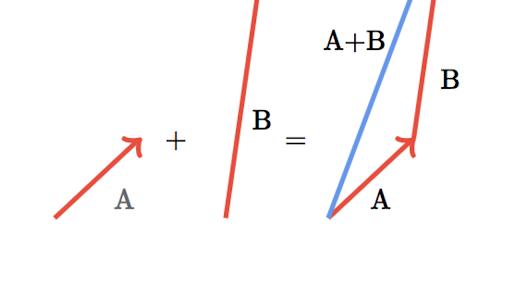
Introduction To Two Dimensional Motion Vector Review Article Khan Two dimensional motion looks at how an object moves in two directions at once. we analyze this motion by separating it into horizontal and vertical components. kinematic equations describe the motion of objects. in two dimensional motion, these are used separately for each component. For two dimensional motion, the path of an object can be represented with three vectors: one vector shows the straight line path between the initial and final points of the motion, one vector shows the horizontal component of the motion, and one vector shows the vertical component of the motion.

Vectors Powerpoint Physics Introduction To Vectors And Two

Comments are closed.